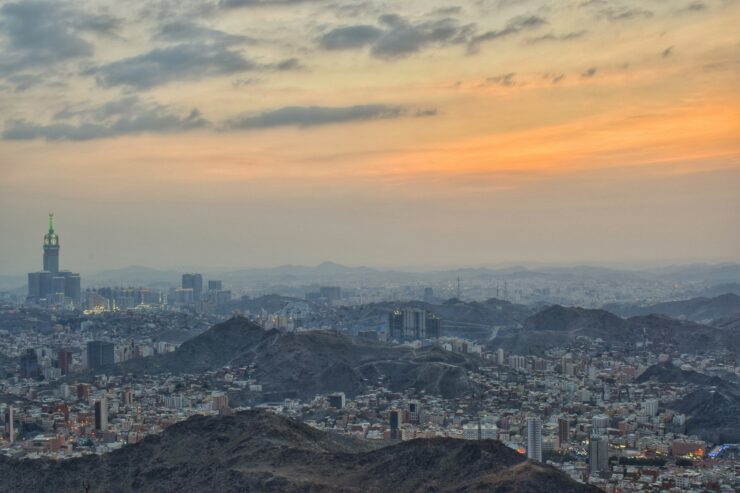
Nestled along the pristine shores of the Red Sea, where the rugged mountains of western Saudi Arabia meet the waters of the Arabian Peninsula, lies a city of profound historical and spiritual significance: Makkah, or Mecca.
This ancient city, with its rich tapestry of culture, tradition, and faith, holds a unique allure for travelers from around the world. Whether you are a devout Muslim embarking on a sacred pilgrimage or a curious adventurer seeking to explore the city’s diverse heritage, there is no shortage of enchanting places to visit in Makkah.
Join us as we embark on a journey through the heart of this remarkable city, uncovering its hidden treasures and delving into its history, culture, and spirituality.
What Is Makkah?
Makkah is a city located in western Saudi Arabia. It is one of the holiest cities in Islam and holds immense religious and historical significance. Makkah is the birthplace of the Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) and the site of the Kaaba, the most sacred structure in Islam, located within the Masjid al-Haram (the Grand Mosque).
Every year, millions of Muslims from around the world visit Makkah to perform the Hajj pilgrimage, which is one of the Five Pillars of Islam and a mandatory religious duty for Muslims who are physically and financially able to undertake it.
Makkah is a place of profound spirituality, and its historical and cultural heritage make it a unique and revered destination for Muslims and a source of fascination for people of all backgrounds.
How Many Days Are Enough in Mecca?
The ideal duration of a trip to Mecca can vary depending on your reasons for visiting and what you wish to experience while you are there. Here are some general guidelines:
- Hajj Pilgrimage: If you are visiting Mecca for the annual Hajj pilgrimage, the duration of your stay will be specified by the Hajj itinerary, typically lasting about 5-6 days. This is a religious obligation for Muslims and includes specific rituals and activities.
- Umrah Pilgrimage: For the Umrah pilgrimage, which is not bound by specific dates like Hajj, a shorter stay of 3-7 days is typical. Umrah can be performed at any time of the year, and the duration depends on your personal preferences and schedule.
- Spiritual Visit: If you are visiting Mecca for a spiritual journey and to spend time in prayer and reflection, you might choose to stay for a longer period, ranging from 7 to 10 days or more. This allows for a more relaxed and immersive experience, with time to visit the Masjid al-Haram and engage in various spiritual activities.
- Tourist Exploration: If you’re interested in exploring Mecca as a tourist, focusing on its historical and cultural aspects, a stay of 2 to 3 days might be sufficient to visit key attractions such as the Masjid al-Haram, the Kaaba, and perhaps explore some of the city’s history and culture.
Religious Places to Visit in Makkah
Here are seven religious places you must visit in Makkah:
Masjid al-Haram
Masjid al-Haram, often referred to as the Grand Mosque, is the most sacred and iconic mosque in Islam, located in the holy city of Makkah, Saudi Arabia.
It surrounds the Kaaba, the central focal point of Islamic worship, and serves as the primary destination for millions of Muslim pilgrims who travel from around the world to perform the Hajj and Umrah pilgrimages.
Masjid al-Haram is not only a place of worship but also a symbol of unity, devotion, and the core of Islamic faith.
The mosque is an architectural masterpiece, characterized by its vast size and awe-inspiring design. Its most prominent feature is the Kaaba, a cube-shaped structure at the center of the mosque, around which Muslims from all corners of the world perform the Tawaf, circumambulating it seven times as an integral part of their pilgrimage rituals.
Masjid al-Haram is not just a place of religious significance but also a symbol of unity for the global Muslim community, as it is the direction (qibla) that Muslims face during their daily prayers, emphasizing their collective devotion to the one true God, Allah.
The annual Hajj pilgrimage is the most profound expression of this unity, as millions of pilgrims converge at Masjid al-Haram to fulfill their religious obligations and seek a deeper connection with their faith.


The Black Stone
Located within Masjid al-Haram, embedded in the Kaaba, the Black Stone, or “Hajar al-Aswad,” is a timeless symbol of faith and spiritual purification in Islam. Its history is deeply intertwined with the faith’s origins, as it is believed to have been a gift from the angel Gabriel to the Prophet Ibrahim.
Over time, the stone transformed from its original white color to a deep, dark hue, a transformation attributed to its absorption of the sins of those who touched it. This transformation is a powerful reminder of the human capacity for forgiveness and renewal, echoing the central theme of repentance in Islam.
For Muslims, the Black Stone is a tangible connection to the Kaaba and its profound significance. Pilgrims from around the world make their way to Makkah to engage in the Tawaf, where they aim to touch or kiss the stone with deep devotion.
This act is a symbolic gesture of humility, submission, and an acknowledgment of the unity of the global Muslim community. It signifies the spiritual journey of cleansing one’s soul and seeking forgiveness, as well as a physical link to the historical and religious heritage of Islam.


The Cave of Hira
The Cave of Hira is situated on the outskirts of Makkah. It is within this cave that the Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) received his first revelations from Allah through the angel Gabriel, marking the beginning of the prophethood and the revelation of the Quran.
The event, known as the first revelation or “Iqra” (Read), occurred when Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) was in deep contemplation and seeking solitude in the cave. The revelations in the cave continued over a period of 23 years, constituting the core of the Islamic faith.
The Cave of Hira is a small, austere space, accessible through a narrow, winding path. It is a place of solitude and reflection, attracting countless pilgrims and visitors who seek to connect with the spiritual journey of the Prophet (SAW) and the divine message he received.
The cave is a site of deep reverence and contemplation, where Muslims can reflect on the beginnings of Islam and the transformative experience that occurred within its confines.
Pilgrims often make the journey to the Cave of Hira, not only to witness the historical significance but also to gain a deeper understanding of the Prophet’s (SAW) spiritual journey and the divine revelations that have shaped the faith of over a billion Muslims worldwide.


Mina
Mina, a valley located a few kilometers east of Makkah, holds a pivotal role in the annual Islamic pilgrimage of Hajj. Muslim pilgrims gather here during the Hajj season, making it one of the essential destinations on their sacred journey.
The significance of Mina is rooted in the symbolic rituals that take place here, reminding the faithful of the profound historical events in Islamic history.
Pilgrims spend several days and nights in tent cities in Mina during the Hajj, with accommodations provided by the Saudi government. The most notable ritual performed in Mina is the symbolic stoning of the devil, known as the “Ramy al-Jamarat.”
Pilgrims throw stones at three large pillars representing the temptations of Satan, echoing the actions of the Prophet Ibrahim, who was tempted by Satan but resisted.
Mina’s significance extends beyond the rituals; it serves as a profound reminder of the pilgrims’ submission to Allah and their dedication to their faith. The valley of Mina, with its historical and spiritual resonance, is an integral part of the Hajj experience, providing a meaningful connection to the core principles of Islam.


Safaa and Marwa
Safaa and Marwa are two small hills located within the Masjid al-Haram in Makkah, Saudi Arabia. These hills are of great religious significance to Muslims, as they are integral to the rituals of the Hajj and Umrah pilgrimages.
Their importance is deeply rooted in the history of Hagar and her son, Isma’il, and their quest for water in the arid desert.
According to Islamic tradition, when Hagar and Isma’il were left in the desert by the Prophet Ibrahim (AS), they faced severe thirst. In search of water, Hagar ran between the two hills, Safaa and Marwa, seven times, in a desperate attempt to find sustenance for her infant son.
Her unwavering faith and determination touched the heart of Allah, and a spring of water, known as the Zamzam Well, miraculously gushed forth at the feet of the baby Isma’il.
This act of running between Safaa and Marwa is commemorated by Muslim pilgrims during the Sa’i ritual as an essential part of their Hajj and Umrah. Pilgrims reenact Hagar’s actions by walking seven times back and forth between these two hills.
It symbolizes the devotion, trust, and patience exemplified by Hagar and Isma’il and serves as a reminder of God’s mercy and provision.
Safaa and Marwa hills are now enclosed within a covered, air-conditioned space, and pilgrims can perform the Sa’i ritual in a comfortable and well-maintained environment.
It is a deeply spiritual experience, allowing pilgrims to connect with the historical roots of their faith and the profound acts of devotion that have shaped the practice of Islam for centuries.


Mount Arafat
Mount Arafat, or “Jabal al-Arafat,” is a sacred and historically significant site located on the plain of Arafat, just outside Makkah, Saudi Arabia. It also plays a central role in the annual Islamic pilgrimage of Hajj and holds great spiritual importance in Islam.
The 9th day of Dhul-Hijjah, the last month of the Islamic lunar calendar, is dedicated to the Day of Arafat, when pilgrims ascend the hill. This day is often considered the most critical part of the Hajj pilgrimage.
It is on this hill that the Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) delivered his farewell sermon during his final Hajj, emphasizing the principles of equality, justice, and the unity of the Muslim community.
Pilgrims who ascend Mount Arafat on the Day of Arafat stand together, engage in supplication, and seek forgiveness from Allah.
The experience of standing on the plains of Arafat is a powerful one, as it represents the moment when Muslims come closest to God, asking for mercy, forgiveness, and guidance.
It is believed that prayers and supplications made on this day are particularly powerful and that the sins of those who sincerely seek forgiveness are forgiven.


Historical Places to Visit in Makkah
Want to delve deeper into the history of the city of Makkah? Here are some historical places in Makkah that should be on your list:
Masjid Jin
Masjid Jin, also known as the Mosque of the Jinn, is a remarkable and spiritually significant place located in Makkah, Saudi Arabia. It has a unique standing in Islamic tradition due to its association with the supernatural beings known as jinn.
This small mosque stands on the outskirts of Makkah and is named after the belief that the Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) was once heard reciting the Quran here, and a group of jinn is said to have listened to his recitation.
The mosque is situated at a distance from the heart of the city, offering a serene and tranquil atmosphere. It features simple architecture and is often visited by pilgrims and tourists seeking to connect with the supernatural occurrences of Islamic history.
The belief that the Prophet’s (SAW) recitation attracted the attention of the jinn serves as a testament to the extraordinary nature of his prophethood.
The stories associated with Masjid Jin underline the inclusive nature of Islam, where even supernatural beings are said to have listened to the message of monotheism.
As such, this mosque serves as a reminder of the universal message of Islam, accessible to both human and supernatural beings. It is a place of reflection and wonder, where visitors can contemplate the miracles of the faith and the transformative power of the Quranic message.


The Well of Zamzam
Wondering what is the famous well in Makkah? The “Well of Zamzam,” located within the Masjid al-Haram in Makkah, Saudi Arabia, is one of the most renowned and sacred wells in the Islamic world. The Well of Zamzam is highly revered by Muslims and holds immense historical and religious significance.
According to Islamic tradition, the well was miraculously provided by Allah to quench the thirst of Hagar and her son, Isma’il, the wife and son of the Prophet Ibrahim (Abraham). The name “Zamzam” is said to originate from the sound of water gushing forth when Isma’il’s heels scraped the sand.
Zamzam water is believed to be pure and blessed, and it is customary for pilgrims and visitors to the Masjid al-Haram to drink from the well, seeking spiritual purification and blessings. The act of drinking Zamzam water is considered a special ritual, and many pilgrims carry bottles of it back to their home countries as a sacred relic.
The Well of Zamzam is a symbol of divine providence and a source of spiritual nourishment for Muslims. It not only quenches physical thirst but also serves as a reminder of the miraculous blessings of God and the deep connection between believers and the historical events of Islam’s early days.


Masjid Aisha
Masjid Aisha, also known as the Masjid Taneem, is located a few kilometers away from the Kaaba in Makkah, Saudi Arabia. It holds a special place in the hearts of Muslims, especially for female pilgrims, as it is closely associated with the rituals of the Hajj and Umrah pilgrimages.
For female pilgrims visiting Makkah, Masjid Aisha is the designated site where they put on their Ihram, the white pilgrimage attire, before commencing their Hajj or Umrah.
It is a mandatory step in the pilgrimage process and marks the beginning of the sacred journey. Male pilgrims typically put on their Ihram at various designated points within Makkah itself.
The mosque itself is a simple yet serene structure, with an open courtyard and prayer halls. It is frequented by pilgrims, particularly women, who gather here to perform the Tahallul, which involves changing into the special clothing of Ihram, reciting specific supplications, and declaring their intention for the pilgrimage. T
he mosque is often bustling with a sense of anticipation and spiritual devotion as pilgrims prepare to embark on their sacred journey.


Makkah Museum
The Makkah Museum, also known as the “Makkah Regional Museum,” is a cultural and historical institution located in the holy city of Makkah, Saudi Arabia. This museum is a treasure trove of Islamic heritage, artifacts, and historical relics that provide visitors with a deeper understanding of the rich history and significance of Makkah in the context of Islam.
The museum’s exhibits cover various aspects of Makkah’s history, from the pre-Islamic era to the present day. It showcases artifacts, manuscripts, and archaeological findings, illustrating the city’s evolution through time.
Visitors can explore the life and times of the Prophet Ibrahim, the building of the Kaaba, and the development of Makkah as a center of pilgrimage.
One of the museum’s highlights is the section dedicated to the Hajj pilgrimage, with displays depicting the rituals, traditions, and significance of this annual Islamic journey.
The museum also houses rare manuscripts and copies of the Quran, along with historical maps and documents that shed light on Makkah’s development.
The Makkah Museum provides an opportunity for visitors to connect with the profound legacy of Islam and Makkah’s role as the spiritual center of the Muslim world.
The museum not only preserves the city’s heritage but also invites individuals to explore its history and traditions, offering a meaningful and enriching experience for all.
Important Places to Visit in Mecca
Here are some important places to visit in Mecca.
Jannat al-Mu’alla Cemetery
The Jannat al-Mu’alla Cemetery, located in the holy city of Makkah, Saudi Arabia, is a profoundly significant burial ground with deep spiritual and historical importance in Islam.
It is often referred to as the “Garden of Paradise” and serves as the final resting place for numerous prominent figures in Islamic history. The cemetery is a place of reverence, pilgrimage, and reflection, drawing devout Muslims and visitors alike.
Jannat al-Mu’alla is most notably recognized for being the resting place of several close family members and early companions of the Prophet Muhammad (PBUH), including his beloved wife Khadijah bint Khuwaylid, his uncle Abu Talib, and many others.
Their graves are marked by simple structures, and the cemetery holds an air of solemnity and sanctity.
Pilgrims and visitors come to Jannat al-Mu’alla to pay their respects, offer prayers for the deceased, and seek spiritual connection with the pioneers of the Islamic faith.
It is a place for introspection and a reminder of the transient nature of life and the enduring legacy of those who contributed to the early days of Islam. It is a place where the past and the present converge, offering a sense of continuity and a bridge between the living and the departed.


The Clock Tower Museum
The Clock Tower Museum, also known as the “Makkah Clock Tower Museum,” is an intriguing cultural and historical institution located within the Abraj Al Bait Towers complex, adjacent to the Masjid al-Haram in Makkah, Saudi Arabia.
This museum is a captivating fusion of Islamic heritage and modernity, allowing visitors to explore the historical, religious, and technological aspects of Makkah’s development.
The museum is situated within the Abraj Al Bait Towers, one of the world’s tallest buildings, and is famous for its massive clock faces, which can be seen from afar. Inside the museum, visitors can delve into the history of Makkah, the expansion and modernization of the Masjid al-Haram, and the development of the Abraj Al Bait complex.
One of the highlights of the museum is the history of timekeeping in Makkah, where the iconic clock faces are showcased alongside vintage timekeeping equipment. This section underscores the significance of precise timekeeping in the context of the Islamic prayer schedule and the annual Hajj pilgrimage.
The Clock Tower Museum offers an immersive experience that combines technological innovation with the historical and religious roots of Makkah.
Visitors can gain a deeper appreciation of the city’s rich history and its integration of modern technology to serve the needs of the global Muslim community, especially during the annual Hajj pilgrimage and daily prayers.


What Is the Most Visited Place in Makkah?
The most visited place in Makkah is undoubtedly the Masjid al-Haram, also known as the Grand Mosque. It is the holiest site in Islam and the focal point of the city.
Millions of pilgrims and visitors flock to Masjid al-Haram throughout the year, with the numbers significantly increasing during the Hajj pilgrimage season and the Umrah pilgrimage, which can be performed year-round. The mosque’s capacity is continually expanded to accommodate the growing number of visitors.
Places to Visit in Madinah
Madinah is the second holiest city in Islam and holds a special place in the hearts of Muslims worldwide. If you are planning a trip to Madinah, make sure to discover the remarkable sites that make Madinah a unique destination for travelers:
- The Prophet’s Mosque (Masjid al-Nabawi): The second holiest mosque in Islam, housing the Prophet Muhammad’s (SAW) tomb and a place of immense spiritual significance.
- Quba Mosque: The first mosque in Islam, often visited by pilgrims for its historical importance.
- Uhud Mountain: Known for the Battle of Uhud, it offers hiking opportunities and a chance to explore the historical battlefield.
- Qiblatain Mosque: Famous for its two qiblas, it’s a site where the Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) received divine guidance to change the direction of prayer.
- Jannat al-Baqi Cemetery: The burial ground for many of the Prophet’s (SAW) companions and family members.
- The Seven Mosques: These mosques are historically significant for their role in early Islamic history and can be visited as part of a tour.
Can Non-Muslims Go to Mecca?
In general, non-Muslims are not permitted to enter the city of Makkah (Mecca), Saudi Arabia. The Saudi government enforces strict regulations restricting entry into the city.
This restriction is primarily rooted in Islamic religious practices and is meant to preserve the sanctity and security of the holy city. The two holiest cities in Islam, Makkah and Medina, are considered extremely sacred and are reserved for the exclusive use of Muslim pilgrims and worshipers.
There are checkpoints and security measures in place at the entrances to Makkah to ensure that only Muslims with the necessary permits, such as Hajj or Umrah visas, can enter the city.
Non-Muslims who are found attempting to enter Makkah without a legitimate reason may be turned away or face penalties. It’s important for travelers, especially non-Muslims, to be aware of these restrictions and to respect the religious and cultural sensitivities of the region.
Summary – Places to Visit in Mecca
Makkah, Saudi Arabia, is not only the holiest city in Islam but also a city of historical and cultural significance. Here, you can experience a journey through the most revered and iconic sites, from the Grand Mosque (Masjid al-Haram) and the Kaaba to the Well of Zamzam and the Cave of Hira.
The historical and religious importance of these places makes Makkah a profound destination for Muslims. Whether you are planning a pilgrimage, interested in Islamic history, or simply curious about Makkah’s heritage, the city offers a glimpse into the spiritual and cultural treasures